Enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the public procurement system through robust monitoring and evaluation practices holds significant potential for achieving substantial savings and ensuring the optimal use of public funds. The Public Procurement Regulatory Authority (PPRA), under its enabling Act, is empowered to monitor and evaluate the entire procurement process across the country. This oversight provides stakeholders with valuable insights into the transparency, accountability, and value for money associated with public procurement activities. Procurement monitoring is a key function within the broader procurement regulatory framework. It ensures transparency, efficiency, accountability, and compliance in public procurement processes.
Core Functions of Procurement Monitoring
- Compliance Verification:
- Ensures that procuring agencies follow the rules, procedures, and thresholds set in the Public Procurement Rules, 2004, regulations and instructions issued by the Authority.
- Reviews tenders, evaluation reports, and contract awards for adherence to legal requirements.
- Performance Tracking:
- Assesses how effectively public procurement contributes to value for money and service delivery.
- Evaluates procurement timelines, cost-efficiency, and bidder participation.
- Data Collection and Reporting:
- Gathers procurement data from public entities for analysis and policy-making.
- Provides feedback to government bodies.
- Capacity Building and Advisory:
- Highlights gaps or recurring issues in procurement practices.
- Informs training, policy revisions, or regulatory updates.
- Transparency, Early Warning and Risk Management:
- Identifies red flags such as excessive direct contracting or repeated procurement delays.
- Helps initiate corrective actions before major failures occur.
- Reduces risk of corruption or mismanagement.
PPRA is currently undertaking a significant initiative to modernize and streamline the federal public procurement system. This reform is guided by the objectives of aligning procurement practices with international best standards and fulfilling the commitments of the Government of Pakistan. The overarching aim is to cultivate a more efficient, transparent, and competitive procurement environment, ultimately contributing to improved financial management and optimized public sector outcomes.
Monitoring and evaluation within the public procurement process is conducted at two distinct levels: the procuring agency level and the regulatory authority level. Procuring agencies bear the primary responsibility for overseeing and assessing their procurement activities over a defined period. The frequency and scope of these monitoring exercises are determined by the respective entities. Importantly, all reports generated through these monitoring and evaluation processes must be uploaded to the e-Pak Acquisition & Disposal System (EPADS) for review by the regulatory authority. This practice promotes transparency and enables the regulatory authority to assess the agency’s compliance with applicable procurement regulations.
At the regulatory level, the responsibility lies in overseeing and guiding the overall procurement process to ensure consistency with the established regulatory framework. The regulatory authority is tasked with ensuring that procuring agencies adhere to applicable procurement rules and procedures. A key function includes the thorough review of monitoring and evaluation reports to verify compliance and identify areas for improvement. Procuring agencies are required to develop monitoring plans, which must also be uploaded to the e-Pak Acquisition & Disposal System (EPADS). This regulatory oversight mechanism provides an additional layer of accountability and strengthens transparency across the procurement process.
By implementing this two-tiered approach to monitoring and evaluation, and by sharing the results through the e-Pak Acquisition & Disposal System (EPADS), a robust system of checks and balances is established to enhance transparency and accountability in procurement processes.
M&E ensures a continuous flow of information, serving as a vital management tool for procurement professionals to monitor progress, identify challenges, and evaluate performance. It plays a critical role in identifying weaknesses and deficiencies, thereby enabling timely corrective actions. An effective M&E system fosters a culture of transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement across public sector organizations.
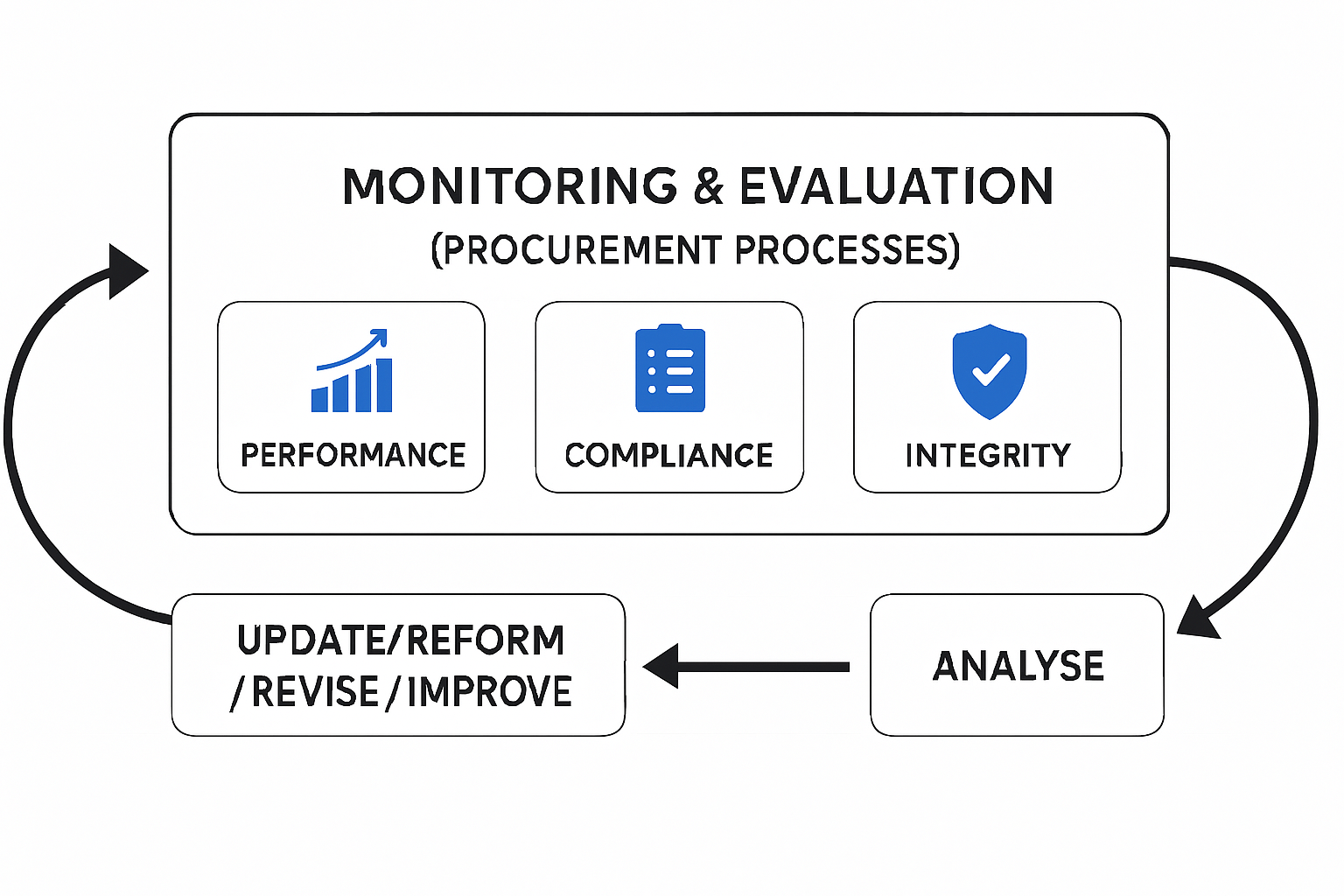
As a macro-level monitoring approach, the Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) function of the Authority focuses on three key components: (i) performance, (ii) compliance, and (iii) integrity of procurement processes. Monitoring and evaluation activities, including procurement audits, are to be carried out in accordance with key performance indicators and procedures established by the Authority. Based on the findings, procuring agencies, in collaboration with the regulatory authority, critically assess existing gaps and deficiencies and propose remedial measures to strengthen and enhance the procurement system.